Design Thinking
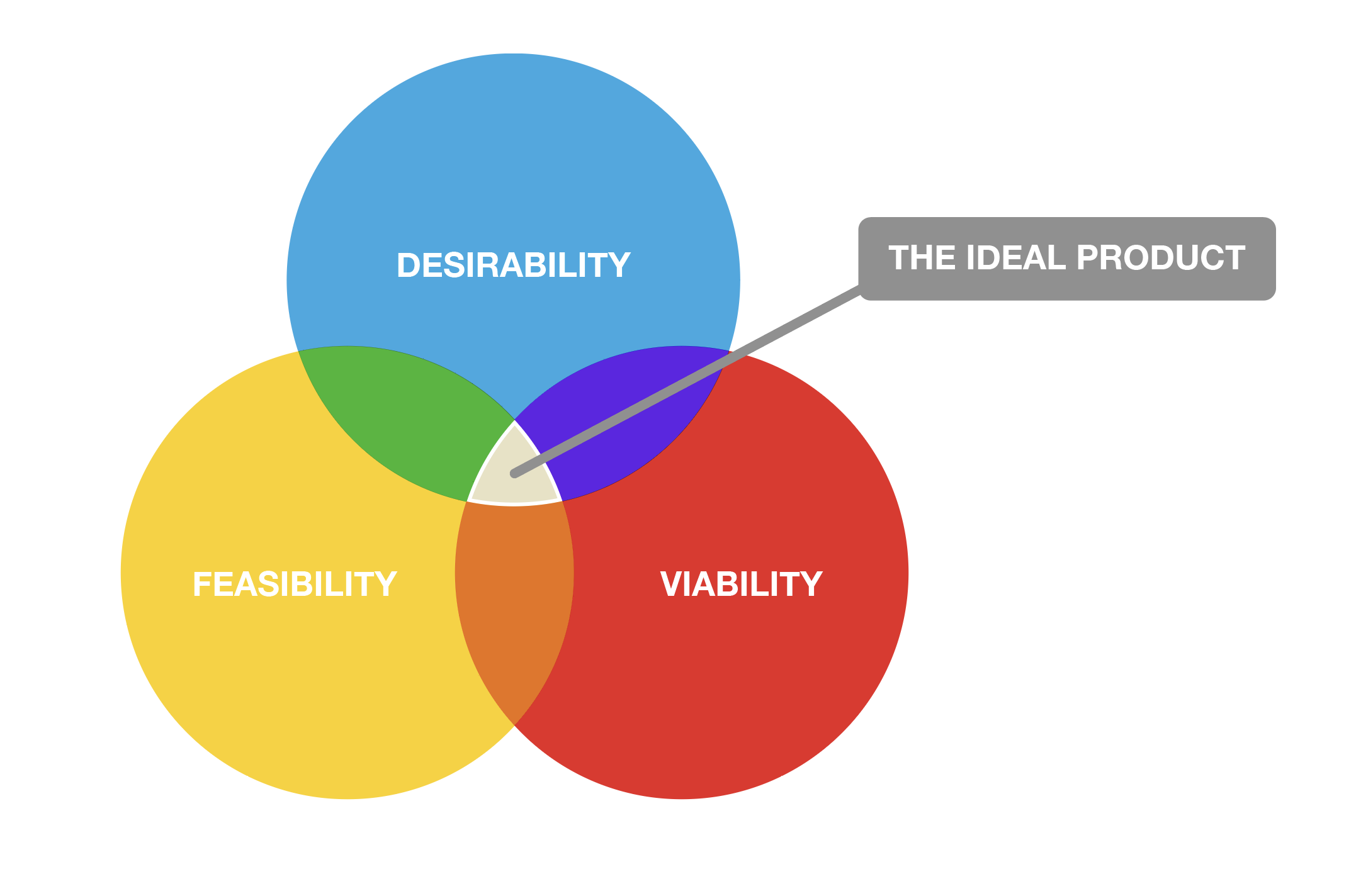
The thought process known as ‘design thinking’ has been around in some form since the 1960’s. But the concept wasn’t really socialized until the 1990’s by a university in the Netherland’s. The basic concept is an approach to look at these three concepts: Desirability, Feasibility, and Viability then, we have to find the sweet spot where all three needs are met.
Desirability — Does the solution create a desirable experience?
Feasibility — Can our team pull this off?
Viability — Will our team be successful if we do this?
With this way of thinking the first place we start is desirability. We try and think about all the options that would benefit the user and create an experience that brings value to the user. In this process there are five steps:
Build empathy for the user with your team. Conduct interviews, understand the users pain points.
Identify your users needs and pain points by listening to them and understanding their experiences.
Create solutions that might solve the customers problems by ideating
Workshop a way to bring these ideas into a viable and feasible space
User test your ideas with real users! Learn from those tests and iterate from there.
Double Diamond
I use the double diamond approach to explore innovative and creative ways to solve user problems and to understand their pain points. This approach helps you look at a problem with 2 different thinking types.
Divergent thinking - open minded and broad thinking, consider all the options
Convergent thinking - identify a few key pain points and solutions
So what does this mean? Well, there are 4 steps to Design Thinking:
Discover the users pain points.
Define particular pain points.
Develop possible solutions to those pain points.
Deliver feasible and viable solutions to these pain points for the user.
Discover
In the first part of this process, I encourage people to practice divergent thinking. The important part here is to keep an open mind and explore all the options, constrained by nothing. We get out of the office, away from our home base, and talk to our users. We can do that through phone calls, video conferences, or in person. Interview them and watch them use the product. The most important thing in this stage is to listen. Hear what the user is saying. The main goal here is to build empathy.
When we feel like we have enough empathy for the user, we create documentation of what we’ve learned and most importantly, what we’ve heard by creating empathy and customer journey maps.
Define
Once we understand the pain points the users are dealing with, how they feel about it, and what they do, it’s time to start thinking with convergent thinking. Creating a plan that takes specific experiences within the pain points mentioned and tries to add delight. This can be done in a lot of ways my team leverages the ‘Rose, Thorn, and Bud’ activity.
Develop
We are a the mid-way point of the double diamond now and we have determined the problem statement(s) for a project. Now we will go back to divergent thinking. In developing an idea to solve our problem statement we try to come up with big, amazing, creative ideas. As a team we brainstorm ideas — and as we all know, there are no bad ideas in brainstorming. One of my favorite ways to develop ideas is through the Crazy 8’s activity.
Deliver
You might have guessed, that in this part of the process we switch back to convergent thinking. The most important thing to do here is to make sure we pitch an idea that is achievable — something we can actually develop and deliver value to the user. Dot voting or prioritization voting is one of my preferred ways of thinking through this — especially with all the stakeholders: business owners, product managers, engineers, researchers, and product designers. It’s important to have many different types of stakeholders in the room for this voting so product designers can get an idea of where the business owners’ mind is at for the solution. It also helps people level set for how the solution will be developed.
Once I have an idea of what the feasible ideas are, I prefer to put all the ideas on a priority matrix in order to know the scale of value for the user vs. difficulty to accomplish.
What’s next?
After you create these ideas it’s time to make wireframes to user test with actual users, learn everything you can with those tests and then iterate!